The human body is a complex collection of different systems working together.
To understand and explain the complex workings of the human body, it is important to use the correct terminology in relation to:
- location, direction and planes
- cavities
- cells, tissues and organs.
Location, direction and planes
Anatomy uses a specific set of terminology to explain how the body works and to describe the location of different parts of the body. If a client is describing a pain or feeling unwell, you need to be able to communicate this information, orally and in writing, to your supervisor, nurse or doctor so they can investigate. For instance, a person's pain can be described as 'abdominal' pain. You must communicate accurately using a 'shared' language that is understood by every one.
Anatomical planes are imaginary ‘slices’ or planes cut through the body used to describe the location of body structures. They are applied when the human body in the anatomical position - see the diagram below. This is the standard reference orientation of the human body.
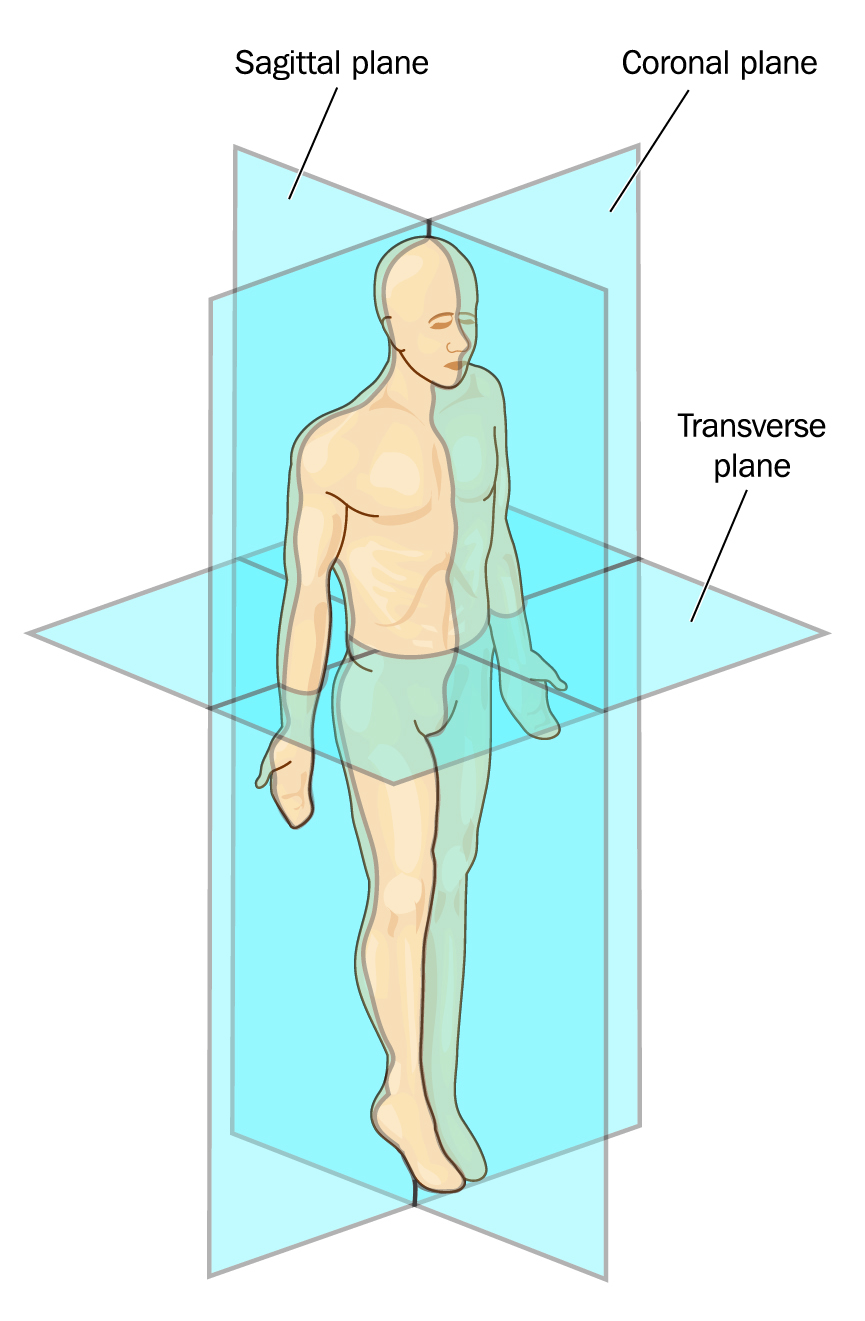
Image by Blamb, Shutterstock, Shutterstock licence
 Select to learn more
Select to learn more
Select each bar to expand and reveal further information about the different planes of the body.
Anatomical directions and locations
The following table has common terminology used in anatomy that explains the location and direction of structures within the body.
| Anatomical Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Superior | Towards the head |
| Inferior | Towards the feet |
| Anterior (ventral) | Towards the front |
| Posterior (dorsal) | Towards the back |
| Medial | Towards the middle of the body |
| Internal (deep) | Away from the surface of the body |
| External (superficial) | Towards the surface of the body |
| Proximal | Towards the trunk (main mass) of the body |
| Distal | Away from the trunk (main mass) of the body |
| Lateral | Towards the side of the body |
 Check your understanding
Check your understanding
Fill in the blanks by dragging the words into the correct place then select ‘Check’ to see if you are correct. Select the 'Next' button to move to the next questions, then select 'Check' each time for feedback.
Cavities
Cavities are spaces in the body that hold important body parts called organs for example, the heart, lungs and brain. The cavity protects the organs with fluid and a membranous and/or bony structure that gives them space to function.
 Select to learn more
Select to learn more
Select the items on the image to reveal more information about cavities within the body.
Image by VectorMine, Shutterstock, Shutterstock licence
 Important
Important
The dorsal body cavity contains the cranial cavity and the spinal canal.
The ventral body cavity contains the thoracic, abdominal and pelvic cavities.
The building blocks of the human body
The body is made up of ‘building blocks’ called cells that form tissues, bones, blood, organs and organ systems. In order to understand how our organs and organ systems work (the physiology of the body) you must at least have a basic understanding of how the ‘building blocks’ fit together. This is very important when a healthcare team is trying to understand what’s happening in the body and choosing the best way to treat it.
The body is arranged in a hierarchical structure. Each level of organisation depends on the previous layer. Each of the body’s systems are made up of a number of organs. Organs are made up of tissues and tissues are comprised of cells.
Cells
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. They provide structure for the body, metabolise food and convert it into energy.
The human body is composed of trillions of cells. Each cell has many parts called organelles and each has a different structure and function.
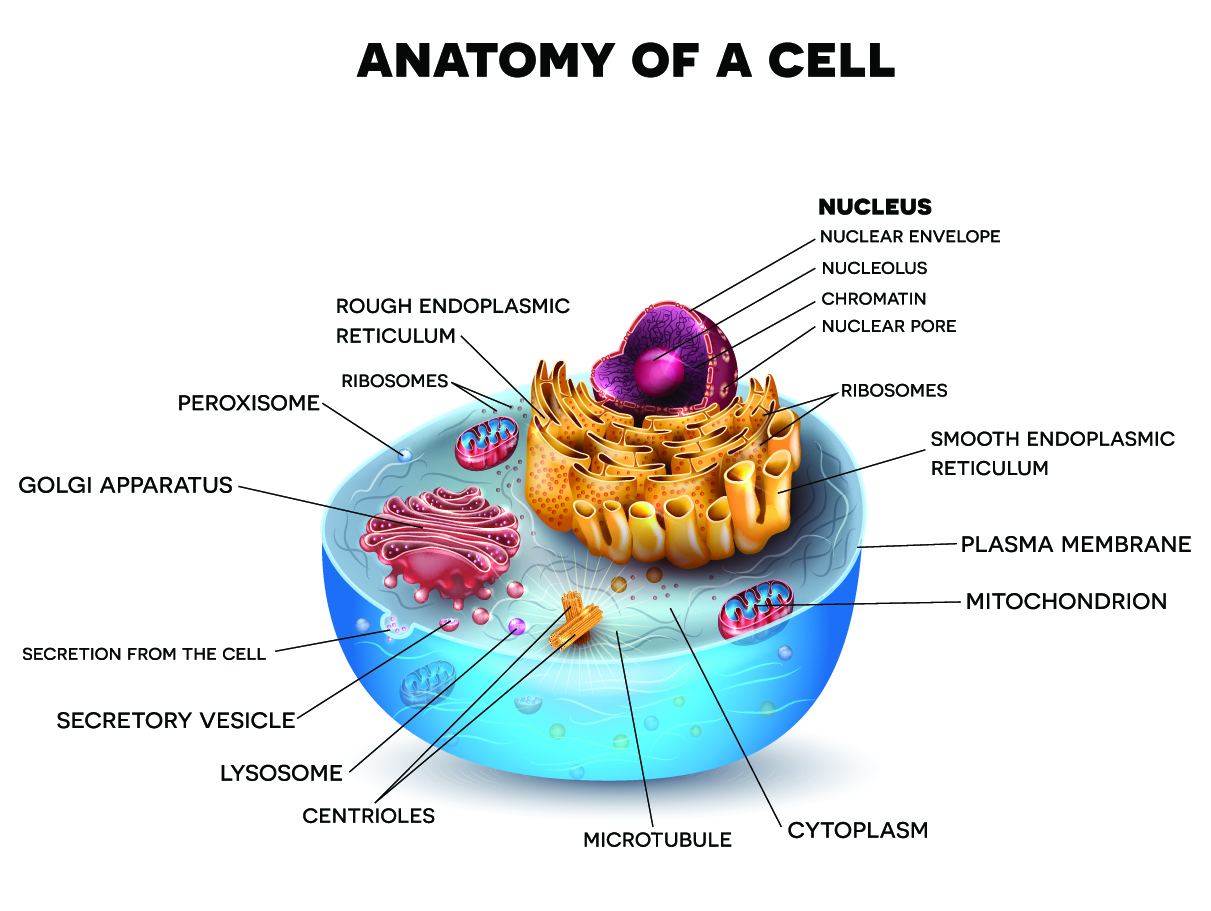
Image by TimeLineArtist, Shutterstock, Shutterstock licence
There are several hundred different types of cells, such as:
- stem cells
- skin cells
- bone cells
- nerve cells
- blood cells
- endothelial cells
- muscle cells
- pancreatic cells
- fat cells
- sex cells.
 Watch the video
Watch the video
Watch
‘Organelles: Structure and
function’ to learn more about cells and organelles.
Reflect on the following questions:
- What are the eight major organelles?
- Where is your genetic material housed?
- What happens to a mitochondria that is not performing well?
Make notes in your notebook or digital device to refer to later.
Tissues
Tissues are groups of cells that have a highly organised structure and function. Even though there are several hundred cell types in the body, all of them can be grouped into just four main categories of tissue.
The four main categories of tissue are:
- epithelial
- connective
- muscle
- nerve.
 Select to learn more
Select to learn more
Select each bar to expand and reveal further information about tissue cells.
Organs and organ systems
An organ is a self-contained group of tissues that performs a specific function in the body, for example, the heart is an organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
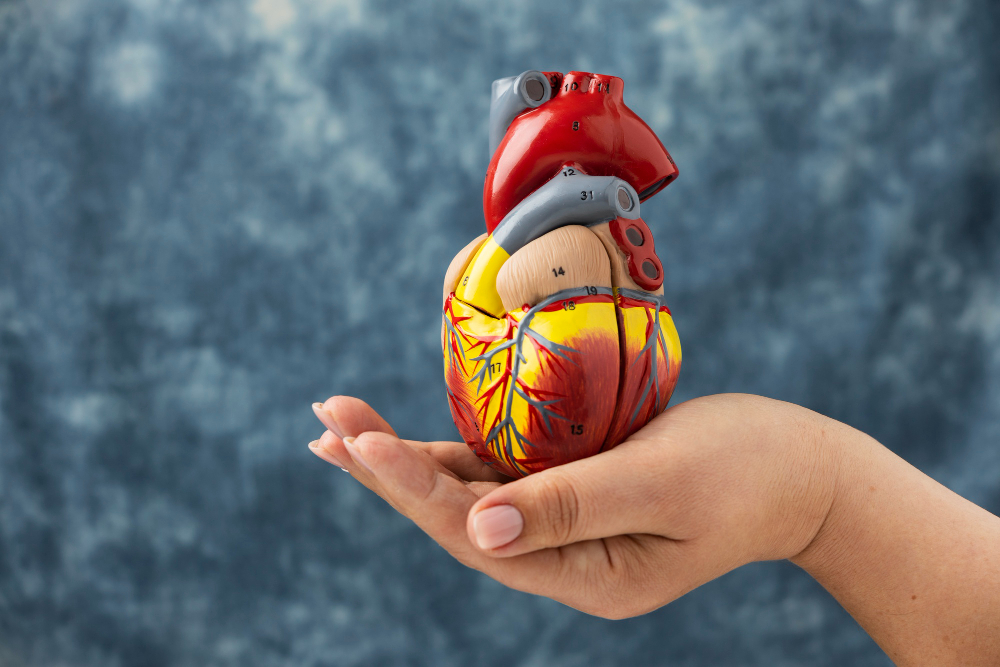

Image by Freepik, Freepik, Licence
Organs are components of organ systems that fulfil the various bodily functions necessary for survival.
There are 11 body systems each with its own function and set of organs. Sometimes the body systems are categorised differently. For example, the male and female reproductive systems can be two different systems and the muscular and skeletal systems as well as the lymphatic and immune systems, can be discussed together. The 11 body systems used in this module include:
- Cardio vascular system
- Respiratory system
- Musculo-skeletal system (including muscular and skeletal systems)
- Endocrine system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system (including the Renal system)
- Reproductive system (including both male and female reproductive systems)
- Integumentary system
- Lymphatic system
- Immune system
- Nervous system (including the Special senses)
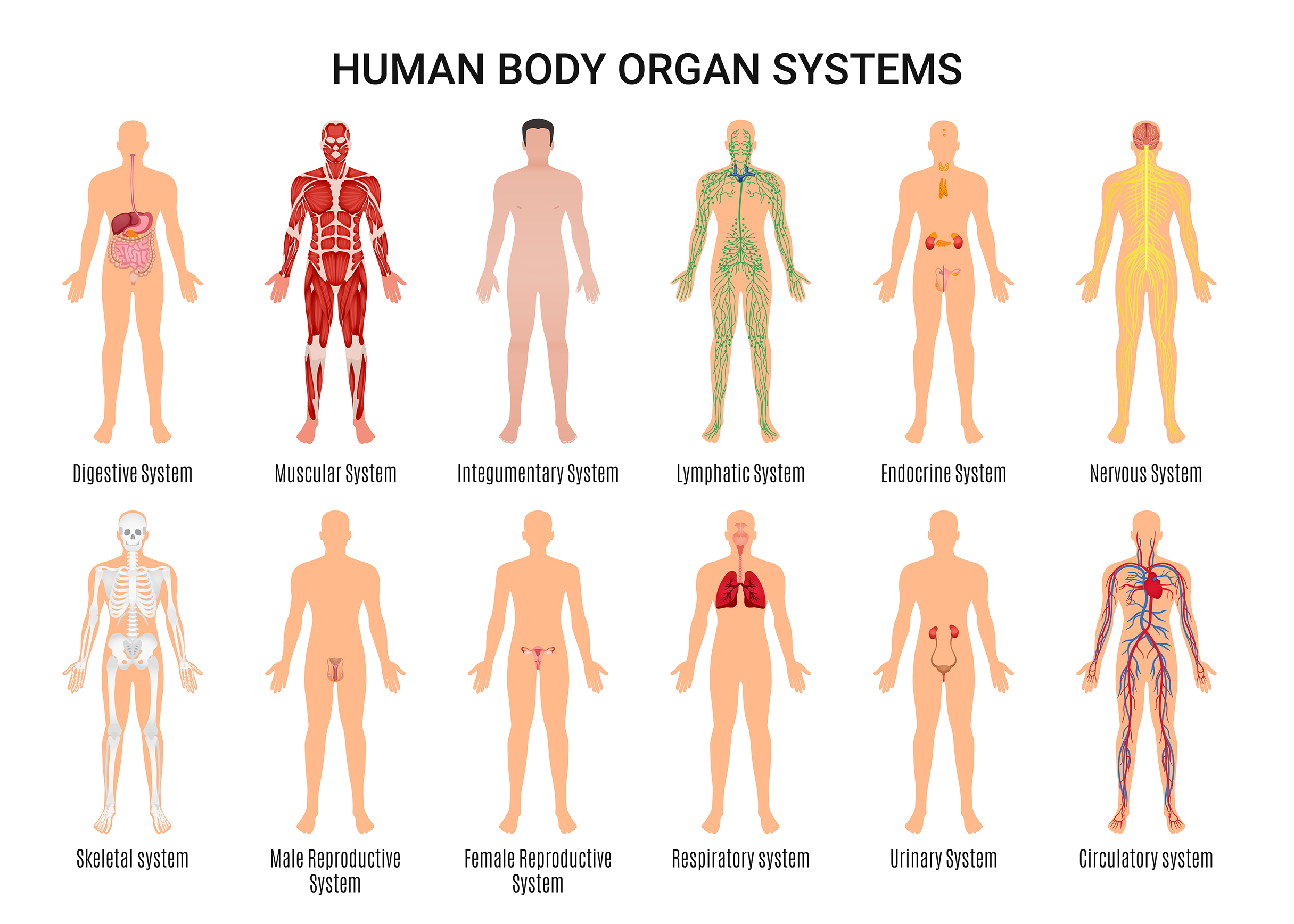
Image by macrovector, Freepik, Licence
 Watch the video
Watch the video
Watch ‘Human body systems functions overview: The 11 champions’ to learn more about the body’s organ systems.
Reflect on the following questions:
- Can you think of a time when your adrenaline kicked in? How did this feel in your body?
- Your tonsils play a significant role in your immune system. Research what happens if they are removed.
- Adults have 206 bones in their bodies. What are their main functions?
Make notes in your notebook or digital device to refer to later.
 Check your understanding
Check your understanding
Respond to the question below and select ‘Check’ to see if you are correct.
Background Colour
Font Face
Font Kerning
Font Size
Image Visibility
Letter Spacing
Line Height
Link Highlight
Text Colour